한국응용과학기술학회 논문 검색

Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lysozyme and Characterization of Antibacterial Peptides
간행물 정보 : Vol. 42 No. 2, 2025년,
파일형식 : pdf






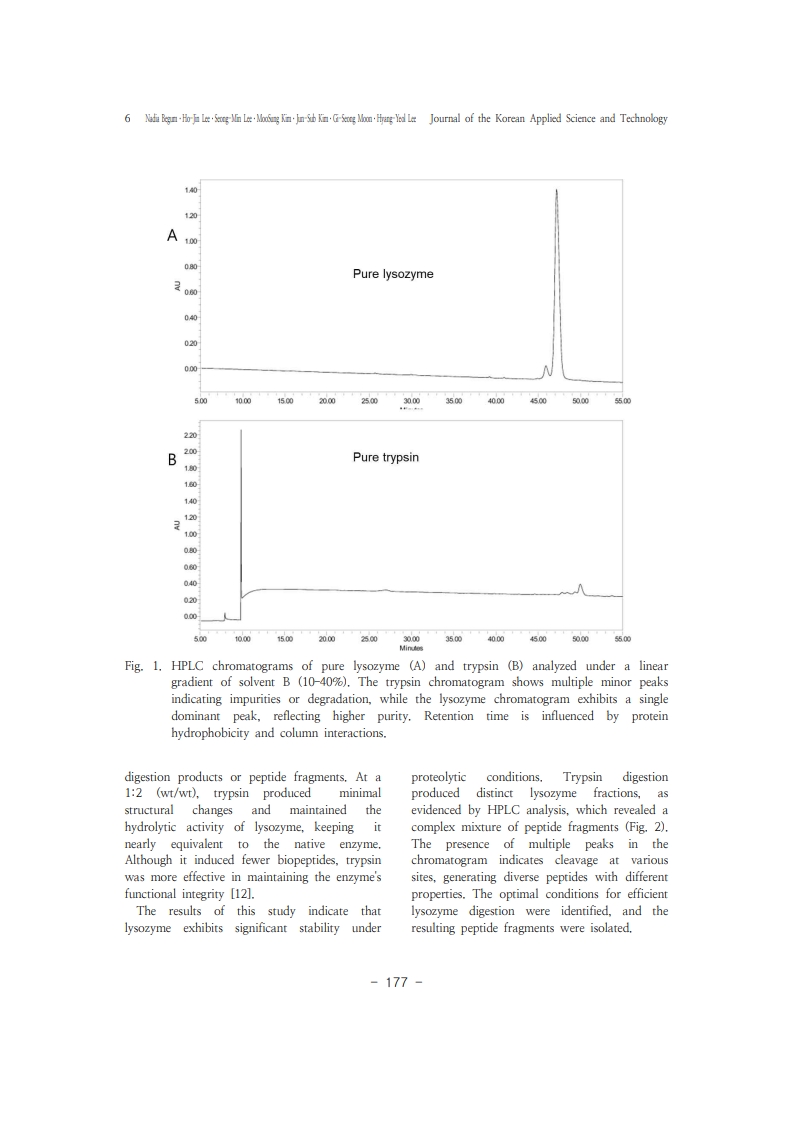
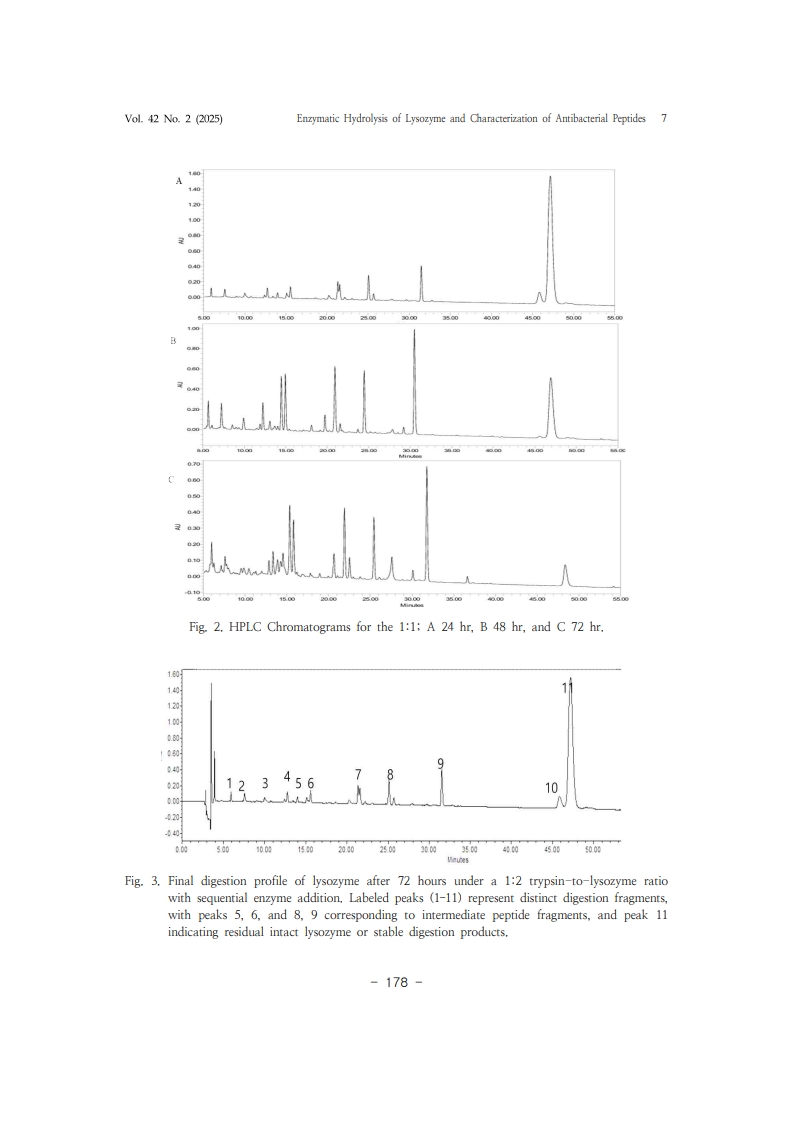

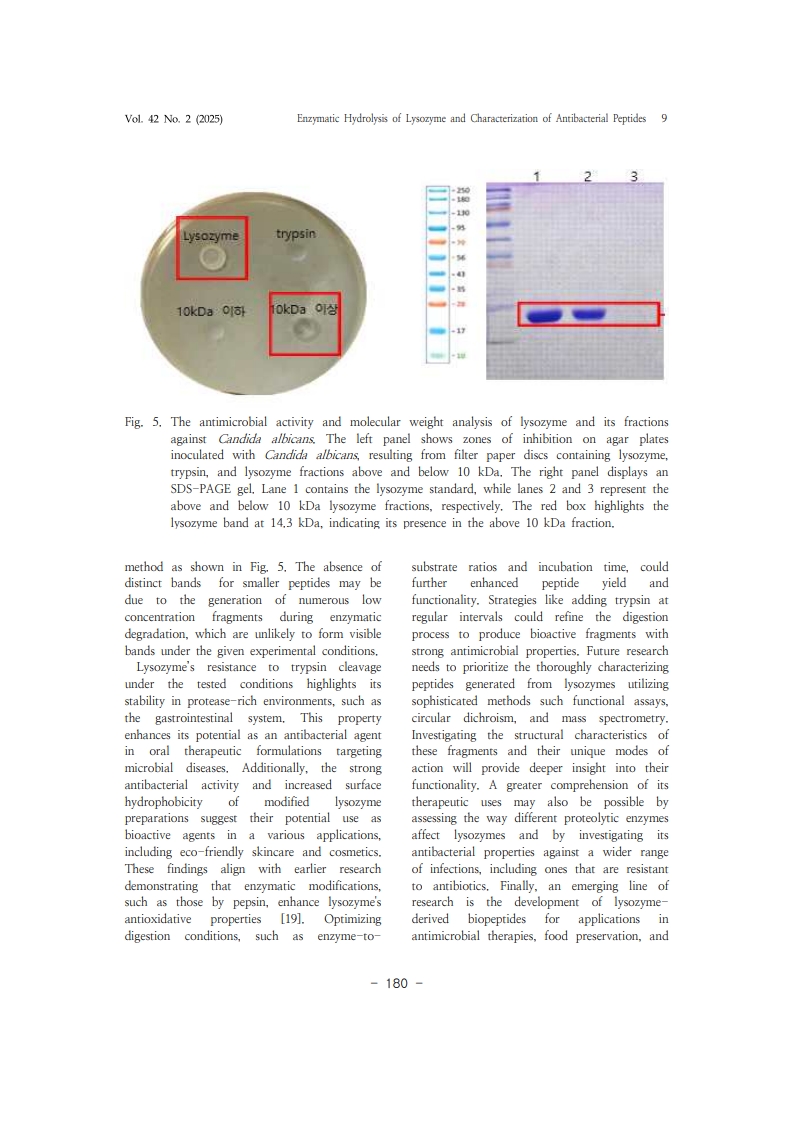



1. Y. Mine, F. Ma, S. Lauriau, “AntimicrobialPeptides Released by Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Hen Egg White Lysozyme", J. Agric. Food Chem., Vol.52, No.5, pp. 1088–Vol. 42 No. 2 (2025) Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Lysozyme and Characterization of Antibacterial Peptides 111094, (2004).
https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0345752
2. W. Carrillo, A. Lucio, J. Gaibor, D. Morales, G. Vasquez, “Isolation ofantibacterial hydrolysates from hen egg white lysozyme and identification of
antibacterial peptides", J. Med. Food, Vol.21, No.8, pp. 808–818, (2017).https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2017.0134
3. X. Zhang, A. Jiang, H. Yu, Y. Xiong, G. Zhou, M. Qin, J. Dou, J. Wang, “Humanlysozyme synergistically enhances bactericidal dynamics and lowers the
resistant mutant prevention concentration for metronidazole to helicobacter pylori by increasing cell permeability", Molecules, Vol.21, No.11, 1435, (2016).
https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21111435
4. P. F. Fox, A. L. Kelly, “Indigenous enzymesin milk: Overview and historical aspects—Part 1", Int. Dairy J., Vol.16, No.6, pp.500–516, (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.idairyj.2005.09.013
5. S. A. Ragland, A. K. Criss, “From bacterialkilling to immune modulation: Recentinsights into the functions of lysozyme", PLoS Pathog., Vol.13, No.9, e1006512,
(2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006512
6. N. Nawaz, S. Wen, F. Wang, S. Nawaz, J. Raza, M. Iftikhar, M. Usman,“Lysozyme and Its Application as Antibacterial Agent in Food Industry",
Molecules,Vol.27, No.19, 6305, (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27196305
7. P. Ferraboschi, S. Ciceri, P. Grisenti, “Applications of lysozyme, an innateimmune defense factor, as an alternative antibiotic", Antibiotics, Vol.10, No.12,
1534, (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10121534
8. L. Jiang, Y. Li, L. Wang, J. Guo, W. Liu, G. Meng, L. Zhang, M. Li, L. Cong, M.Sun, “Recent Insights into the Prognostic and Therapeutic Applications of
Lysozymes", Front. Pharmacol., Vol.12, 767642, (2021).https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.767642
9. E. D. N. S. Abeyrathne, H. Y. Lee, D. U. Ahn, "Sequential separation of lysozyme, ovomucin, ovotransferrin, and ovalbuminfrom egg white", Poult Sci., Vol.93, No. 4, pp. 1001–1009, (2014).https://doi.org/10.3382/ps.2013-03403
10. F. I. Maier, D. Klinger, M. Grieshober, R. Noschka, A. Rodriguez, S. Wiese, W. G. Forssmann, L. Standker, S. Stenger, “Lysozyme: an endogenous antimicrobial
protein with potent activity against extracellular, but not intracellular Mycobacteriumtuberculosis", Med. Microbiol. Immunol., Vol.213, No.1, 9, (2024).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00430-024-00793-0
11. H. N. Hunter, W. Jing, D. J. Schibli, T. Trinh, I. Y. Park, S. C. Kim, H. J. Vogel,“The interactions of antimicrobial peptides derived from lysozyme with model
membrane systems", Biochim. Biophys. Acta., Vol.1668, No.2, pp. 175–189, (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2004.12.004
12. L. Tomczyk, G. Lesnierowski, R. CegielskaRadziejewska,“Lysozyme ModificationUsing Proteolytic Enzymes", Molecules, Vol.28, No.17, 6260, (2023).
https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176260
13. A. M. Abdou, S. Higashiguchi, A. M. Aboueleinin, M. Kim, H. R. Ibrahim,“Antimicrobial peptides derived from hen egg lysozyme with inhibitory effect against Bacillus species", Food Control, Vol.18, No.2, pp. 173–178, (2007).https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28176260
14. C. Nimalaratne, N. Bandara, J. Wu, “Purification and characterization ofantioxidant peptides from enzymatically hydrolyzed chicken egg white", Food
Chem., Vol.188, pp. 467–472, (2015).https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.01412
15. R. Goralczyk, H. Mohajeri, and J. Wittwerschegg, “Compositions comprisinglysozyme hydrolysate for use in keratincontainingtissue", U.S. Patent Application
PublicationUS 2016/0317429 A1 (2016).
16. W. Carrillo, A. Lucio, J. Gaibor, D. Morales, G. Vasquez, “Isolation ofantibacterial hydrolysates from hen egg white lysozyme and identification of
antibacterial peptides", J. Med. Food, Vol.21, No.8, pp. 808–818, (2018).https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2017.0134
17. M. Akbarian, A. Khani, S. Eghbalpour, V. N. Uversky, “Bioactive Peptides: Synthesis, Sources, Applications, and Proposed
Mechanisms of Action", Int. J. Mol. Sci., Vol.23, No.3, 1445, (2022).https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23031445
18. T. Yang, G. Lesnierowski, “Changes in selected physicochemical properties oflysozyme modified with a new method using microwave field and oxidation",
PLoS One, Vol.14, No.2, e0213021, (2019).https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213021
19. L. Tomczyk, G. Lesnierowski, R. Cegielska-Radziejewska, “PhysicochemicalEvaluation of Preparations Obtained as a Result of Enzymatic Modification of
Lysozymes with Pepsin and Trypsin", Biol. Life Sci. Forum, Vol.18, No.1, 48, (2022).https://doi.org/10.3390/Foods2022-12924
20. C. J Nobile, A. D Johnson, "Candida albicans biofilms and human disease",Annu. Rev. Microbiol., Vol.69, pp. 71–92, (2015).
https://doi.org/10.1146/annurevmicro-091014-104330
